Bond ETF Meaning
Bond ETF (Exchange Traded Funds) is a fund that invests in various bands ranging from long-term and short-term to corporate bonds and government securities. Like a mutual fund, the Bond ETF is an exchange-traded fundExchange-traded FundAn exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a security that contains many types of securities such as bonds, stocks, commodities, and so on, and that trades on the exchange like a stock, with the price fluctuating many times throughout the day when the exchange-traded fund is bought and sold on the exchange.read more that invests in a basket of bonds, including government bonds or corporate bondsCorporate BondsCorporate Bonds are fixed-income securities issued by companies that promise periodic fixed payments. These fixed payments are broken down into two parts: the coupon and the notional or face value.read more. The Bond ETF is traded on the exchange, unlike bonds issued in a private placementPrivate PlacementPrivate placement of shares refers to the sale of shares of the company to the investors and institutions selected by the company, which generally includes banks, mutual fund companies, wealthy individual investors, insurance companies.read more or an over the counter market.
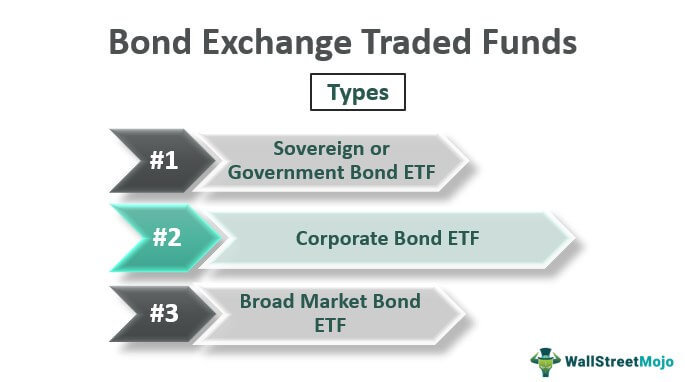
Types of Bond ETFs
Depending on the underlying bondsBondsBonds refer to the debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to acquire investors’ funds for a certain period.read more that the fund invests in, the types can be segregated as below:

You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Bond ETF (wallstreetmojo.com)
#1 – Sovereign or Government Bond ETF
Sovereign or Government Bond ETFs consist of bonds issued by the Government. These investments are rated high since the Government issues them, so the returns on these bonds are slightly lower. As rightly said, the higher the risk, the higher the returns. The interest rates on these securities are way too short, and the tenure of these securities is long.
Examples
- Mortgage Back Securities ETF – These ETFs are backed by a pool of real estate mortgage loans and allow banks to offer mortgages.
- US Treasury ETF – This type of ETF includes the Treasury bonds issued by the US Government, these bear the minimum risk, and hence the returns are also minimized.
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities ETF – As the name suggests, this ETF protects investors from an increase in inflation. The principal value of the fund increases or decreases in line with the CPICPIThe Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the average price of a basket of regularly used consumer commodities compared to a base year. The CPI for the base year is 100, and this is the benchmark point.read more, which means if the inflation shoots, so will the fund’s value.
#2 – Corporate Bond ETF
Corporate Bond Exchange Traded Funds consist of bonds issued by organizations whose proceeds are used for business operationBusiness OperationBusiness operations refer to all those activities that the employees undertake within an organizational setup daily to produce goods and services for accomplishing the company’s goals like profit generation.read more or project refinancing, depending on the organization’s requirement. Since private organizations issue these, the bonds are considered to be risky and hence fetch higher returns. Compared to stocks, bonds are less risky because if the issuer becomes bankrupt, the dues pending for the bondholders are paid before the stockholdersStockholdersA stockholder is a person, company, or institution who owns one or more shares of a company. They are the company’s owners, but their liability is limited to the value of their shares.read more.
Examples
- Investment Grade ETF – Bonds with ratings AAA to BBB are referred to as Investment Grade bonds, which are considered high credit ratings. This means the risk of the issuer default is very low; hence, the return is a bit low compared to other Corporate Bond ETFs.
- Junk Bond ETF – As the name suggests, these are bonds issued by organizations with a weak credit rating and have a higher chance of defaulting. These ETFs have a variety of Junk Bonds and hence offer higher yields, not to mention the risk involved due to the issuer’s credibility.
#3 – Broad Market Bond ETF
This is the most popular type of bond exchange-traded fund since it offers many bonds in one fund, including sovereign bonds to corporate bonds. Since these have various bonds, investing in such funds reduces the risk of completely losing out on the investment, making a pathway for a long-term investment option with returns at regular intervals.
Example
The Unconstrained Bond Exchange Traded Funds allow the fund manager to invest in bonds across geographies, markets, credit ratings, and currencies, allowing the fund to reap the maximum benefits. Since the fund manager has the freedom to invest in any bond they desire, they can look for the bonds with the best returns at the lowest possible cost. The Unconstrained Bond ETF can be more expensive than other Bond Exchange Traded Funds due to this freedom.
Advantages of Bond ETF
The following are the advantages of Bond Exchange Traded Funds.
- Allows investors with limited capital to invest in the bond market, which otherwise can turn out to be a costly affair.
- Limited risk as compared to stocks or mutual funds since the Bond ETFs investETFs InvestETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) are financial instruments formed by combining securities such as stocks and bonds. It is comparable to mutual funds, but such instruments can be purchased or sold at any time during the trading business day.read more in bonds, and in case of bankruptcy, the bondholders are paid before the stockholders.
- Alternative investment option for investors looking to invest in low-risk securities for long-term returns.
- The interest payment is paid monthly, and capital gains are delivered through an annual dividend.
- Even when a specific bond is underperforming, the investor can recover from the investment made in a basket of bonds through Bond ETFs.
- Bond Exchange Traded Funds are available globally.
Disadvantages of Bond ETF
Here we discuss some of the disadvantages of bond Exchange Traded Funds.
- The risk of losing the principal amount is higher in investing in a bond ETF since the Bond Exchange Traded Funds that have no maturity do not guarantee that the total principal amount will be repaid.
- The change in interest rates affects the price of the ETF, making it challenging to mitigate interest rate riskInterest Rate RiskThe risk of an asset’s value changing due to interest rate volatility is known as interest rate risk. It either makes the security non-competitive or makes it more valuable. read more.
- Investing in a Bond Exchange Traded Fund requires sound knowledge about how bonds function. The investor needs to understand whether investing directly in a bond is a better option than investing in a Bond ETF.
- Since it carries a low risk, the returns are minimized compared to the potential returns earned by investing in stocks.
Important Points
- iShares Investment Grade Corporate Bond is the largest Investment Grade Bond Exchange, Traded Fund.
- Some Bond Exchange Traded Funds can be an alternative to money market investment since it provides the flexibility of short and ultra-short-term fixed incomeFixed IncomeFixed Income refers to those investments that pay fixed interests and dividends to the investors until maturity. Government and corporate bonds are examples of fixed income investments.read more ETFs.
- Since the Bond ETFs are exchange-traded like stocks, It has attractive properties like stocks – annual dividends.
- Bond Exchange Traded Funds can be bought and sold in the open market depending on the demand in the market for the ETF.
Conclusion
Bond Exchange Traded Funds are passively managed funds that invest in many fixed-income securities and are traded on an exchange. Bond ETFs charge a lower amount than the actual bond, thereby allowing investors with lower capital to invest in the bonds, which can be pricey. Some Bond ETFs have a pre-determined maturity date ranging from 3 to 10 years and are known as target maturity bond ETFs.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what Bond ETF is. Here we discuss types and examples of Bond exchange-traded funds and their advantages and disadvantages. You can learn more about financing from the following articles –
- Features of Agency Bond
- Dim Sum Bonds
- Compare – Mutual Funds vs ETFs
- ETF vs Index Funds