What is the Future Value of Annuity Due?
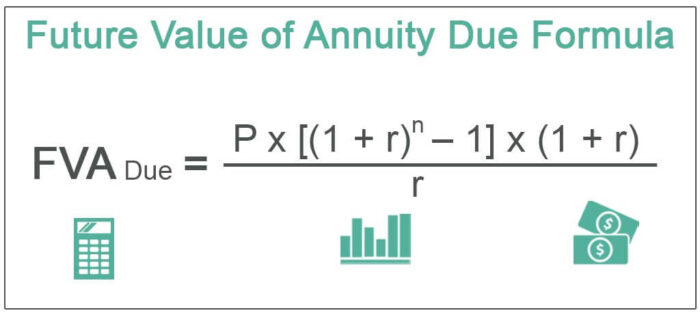
Future value of annuity due is value of amount to be received in future where each payment is made at the beginning of each period and the formula for calculating it is the amount of each annuity payment multiplied by rate of interest into number of periods minus one which is divided by rate of interest and whole is multiplied by one plus rate of interest.
Future Value of Annuity Due Formula
Mathematically, it is represented as,

You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Future Value of Annuity Due Formula (wallstreetmojo.com)
where FVA Due = Future value of an annuity due
- P = Periodic payment
- n = Number of periods
- r = Effective rate of interestEffective Rate Of InterestEffective Interest Rate, also called Annual Equivalent Rate, is the actual rate of interest that a person pays or earns on a financial instrument by considering the compounding interest over a given period.read more
How to Calculate? (Step by Step)
Follow the below steps.
- Firstly, figure out the payments that are to be paid in each period. Please keep in mind that the above formula is applicable only in the case of equal periodic payments. It is denoted by P.
- Next, figure out the rate of interest to be charged based on the prevalent market rate. It is the rate of interest to be received by the investor if the money is invested in the market. To get an effective rate of interest, divide the annualized rate of interest by the number of periodic payments in a year. It is denoted by r. i.e r = Annualized rate of interest / Number periodic payments in a year
- Next, the total number of periods is computed by multiplying the number of periodic payments in a year and the number of years. It is denoted by n. i.e., n = Number of years * Number of periodic payments in a year.
- Finally, the future value of an annuity due is calculated based on periodic payment (step 1), the effective rate of interest (step 2), and a number of periods (step 3), as shown above.
Examples
Example #1
Let us take the example of John Doe, who plans to deposit $5,000 at the beginning of each year for the next seven years to save enough money for his daughter’s education. Determine the amount that John Doe will have at the end of seven years. Please note that the ongoing rate of interest in the market is 5%.

Calculate the FV of annuity due for the Periodic Payment using above given information,

FV of Annuity Due = P * [(1 + r)n – 1] * (1 + r) / r
= $5,000 * [(1 + 5%)7 – 1] * (1 + 5%) / 5%
Future Value of Annuity Due will be –

= $42,745.54 ~ $42,746
Therefore, after seven years John Doe will have $42,746 to spend for his daughter’s education.
Example #2
Let us take another example of Nixon’s plans to accumulate enough money for his MBA. He decides to deposit a monthly payment of $2,000 for the next four years (beginning of each month) so that he is able to gather the required amount of money. As per the education counselor, Nixon will require $100,000 for his MBA. Check if Nixon’s deposits will fund his plans for an MBA, considering the ongoing rate of interest being charged by a bank is 5%.

Given,
- Monthly payment, P = $2,000
- Effective rate of interest, r = 5% / 12 = 0.42%
- Number of periods, n = 4 * 12 months = 48 months
Calculate the FV of Annuity Due for monthly payment using the above-given information,

= $2,000 * [(1 + 0.42%)48 – 1] * (1 + 0.42%) / 0.42%
Future value of Monthly Payment will be –

FV of Annuity Due = $106,471.56 ~ $106,472
So, with planned deposits, Nixon is expected to have $106,472 which more than the amount ($100,000) required for his MBA.
Relevance and Uses
The future value of an annuity due is another expression of the TVMTVMThe Time Value of Money (TVM) principle states that money received in the present is of higher worth than money received in the future because money received now can be invested and used to generate cash flows to the enterprise in the future in the form of interest or from future investment appreciation and reinvestment.read more. The money received today can be invested now that will grow over a period of time. One of its striking applications is in the calculation of the premium payments for a life insurance policy. It also finds application in the calculation of provident fund where the monthly contribution from the salary acts as the periodic payment. The future value of annuity grows based on the stated discount rate. As such, the higher the discount rate, the higher will be the future valueFuture ValueThe Future Value (FV) formula is a financial terminology used to calculate cash flow value at a futuristic date compared to the original receipt. The objective of the FV equation is to determine the future value of a prospective investment and whether the returns yield sufficient returns to factor in the time value of money.read more of the annuity.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to the Future Value of Annuity Due and its meaning. Here we learn how to calculate the FV of an annuity due using its formula along with some practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You may learn more about Financial Modeling from the following articles –
- Tax-Deferred AnnuityTax-Deferred AnnuityA tax-deferred annuity is an employee retirement benefit plan where both an employer and its employee contribute to the saving plan for long-term investment growth. It offers various benefits like age 50 plus catch up, lifetime catch up, taxes, and investment options. Tax-Deferred Annuity = A*[(1+i)n−1] / i read more
- Formula of Deferred AnnuityFormula Of Deferred AnnuityThe deferred annuity formula calculates the present value of the deferred annuity promised to be received after some time. Deferred Annuity = P Ordinary * [1 – (1 + r)-n] / [(1 + r)t * r]read more
- PV of an AnnuityPV Of An AnnuityThe present value of the annuity is the current value of future cash flows adjusted to the time value of money considering all the relevant factors like discounting rate. Thus, it helps investors understand the money they will receive overtime in today’s dollar’s terms and make informed investment decisions.read more
- Annuity vs. PensionAnnuity Vs. PensionAnnuity refers to a contract in which a person agrees to receive regular payments from an insurance company after a specified period of time as per the agreement/contract entered. A pension, on the other hand, is a fixed monthly benefit paid upon retirement when an employee has contributed to a pension fund maintained by the employer during his period of service.read more